Updated on Kisan Patel
The let keyword in C# allows you to store the result of a sub expression in a variable that can be re-use in the query.
So, Using let clause you can reuse the same expression many times in the same query and you don’t need to define it every time you use it.
A let clause introduces a range variable and assigns a value to it.
For Example,
var names = from n in names
where n.Length > 3
let u = n.ToUpper()
where u.EndsWith("Y")
select u;
Here, A where cluase can appear more than once in a query, and it can be interspersed with let clauses.

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace ConsoleApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List persons = new List{
new Person{ Name = "Kisan", City="Ladol" },
new Person{ Name = "Ravi", City = "Ladol" },
new Person{ Name = "Ketul", City = "Vijapur" },
new Person{ Name = "Kisan", City = "Vijapur" },
};
var query = from p in persons
let lname = p.Name.ToLower()
where lname == "kisan"
select new { lname, p.City};
foreach (var name in query)
Console.WriteLine(name.lname + " - " + name.City);
}
}
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
}
}
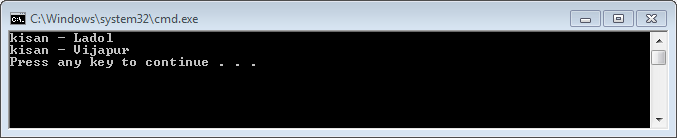
the output of the above C# program…