Updated on Kisan Patel
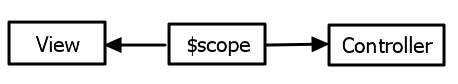
In this tutorial, you learn Views, Modules, Controllers and Scope. The Scope takes care communication between the View and Controller.
First, We define a module in AngularJS as follows:
<script type="text/javascript">
var mymodule = angular.module('module_name', []);
</script>
Then you need to define module using ng-app directive as shown:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app="module_name"> <head> ...
In a module you can define controller, service property, function and etc.
Here’s an example of a really simple controller called, sayhelloController. You’ll see that we pass $scope. This is dependency injection that’s built into AngularJS.
<script type="text/javascript">
var mymodule = angular.module('module_name', []);
mymodule.controller("sayhelloController", function($scope){
$scope.name = 'Your Name';
});
</script>
What this is going to do is Angular, when this controller gets used, will automatically inject a $scope object in. What this controller can do then is serve as the source of the data for the view.
<div ng-app="module_name">
<div ng-controller="sayhelloController">
<p><input type="text" ng-model="name"></p>
<p><b>{{ name }}</b>, how are you?</p>
</div>
</div>
See the Pen dYMPrG by Kisan (@pka246) on CodePen.
Here, we are going to add a name property to $scope. Form here it’s standard data binding : we bind the name property to HTML input control.