Updated on Kisan Patel
There are several operators allowed in C# programming language.
| Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Add |
| − | Subtract |
| * | Multiply |
| / | Divide |
| % | Modulo |
| ++ | Increment by 1 |
| −− | Decrement by 1 |
The below C# program uses these arithmetic operators.
using System;
namespace VariableDemo
{
class OperatorDemo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum, substract, multiply, division, modulo;
int num1 = 30;
int num2 = 10;
int num3 = 3;
sum = num1 + num2;
substract = num1 - num2;
multiply = num2 * num3;
division = num1 / num3;
modulo = num2 % num3;
Console.WriteLine("The sum of num1 and num2 is " + sum);
Console.WriteLine("The difference of num1 and num2 is " + substract);
Console.WriteLine("The multiplications of num2 and num3 is " + multiply);
Console.WriteLine("The division of num1 by num3 is " + division);
Console.WriteLine("Reminder when {0} is divided by {1} is {2}",num2, num3, modulo);
num1++;
num2--;
Console.WriteLine("num1 = {0}, num2 = {1}", num1, num2);
}
}
}
Output of the above C# program…
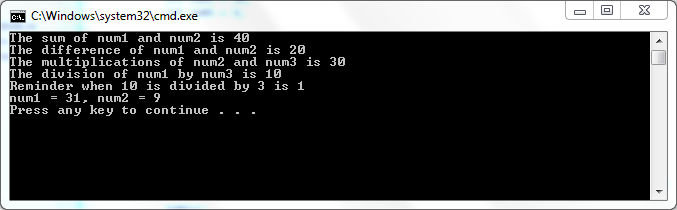
Explanations of Example
Console.WriteLine("Reminder when {0} is divided by {1} is {2}",num2, num3, modulo);
you can see in above line, the Console.WriteLine() method, we have used format-specifiers {int} to indicate the position of variables in the string.
Here, {0}, {1} and {2} will be replaced by the values of the num1, num2, modulo variables.
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
The equals(=) operator is used to assign a value to an object.
For example, we have seen int i = 30; assign the value 30 to the i variable of integer type.
Relational operators are used for comparision purposes in conditional statements.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Equality check |
| != | Un- Equality check |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
Relational operators always result in a Boolean statement; either true or false.
For example if we have two variables
int num1 = 5, num2 = 6;
Then
num1 == num2 // false num1 != num2 // true num1 > num2 // false num1 < num2 // true num1 <= num2 // true num1 >= num2 // false
These operators are used for logical and bitwise calculations.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND |
| | | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR |
| ! | Bitwise NOT |
| && | Logical AND |
| || | Logical OR |
The operators &, | and ^ are rarely used in usual programming practice. The NOT operator is used to negate a Boolean or bitwise expression.
bool a = false; bool b = !a; // b = true
Logical operators && and || are used to combine comparisons.
int i = 3, j = 6; bool result; result = i > 3 && j < 5 // result = false;